Boosting Efficiency and Cutting Costs in Coal Transport: A Peer Group Comparison
Scope For This Project
Coal has been used as a source of energy for thousands of years, and it continues to play a crucial role in modern energy production. However, the process of coal mining and transportation of coal can have significant environmental and social impacts, and it is important to understand these impacts in order to mitigate them effectively.
Table of Contents
Coal Mining
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the earth. There are two main methods of coal mining: surface mining and underground mining. In surface mining, large machines remove the topsoil and rock overlying the coal seam, exposing the coal. The coal is then extracted using machines or explosives. In underground mining, miners use tunnels and shafts to access the coal seam and extract the coal.
Coal mining can have significant environmental impacts, including land disturbance, soil erosion, and water pollution. Surface mining can also result in the loss of biodiversity and habitat destruction. In addition, coal mining can have significant social impacts, including the displacement of communities and the loss of cultural heritage.
Transportation of Coal
Coal is a valuable source of energy, and it is used to generate electricity in power plants all over the world. In order to transport coal from mines to power plants and other facilities, various methods are used, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Trucking
One of the most common methods of transporting coal is by truck. This is especially true for short distances, such as from a mine to a nearby power plant. Trucks can carry large volumes of coal, and they are highly flexible, as they can travel on roads that may not be accessible to other types of vehicles.
However, trucking coal can be expensive, and it can result in significant emissions of air pollutants, including particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide. In addition, trucking can be affected by traffic congestion, accidents, and other logistical challenges.
Trains
Trains are a popular method of transporting coal over longer distances, especially in countries with well-developed railway systems. Trains can carry large volumes of coal, and they are generally more fuel-efficient and less polluting than trucks. Trains can also be highly reliable, as they are less affected by traffic congestion and other logistical issues than trucks.
However, trains can also cause noise pollution and disrupt wildlife habitats. In addition, train derailments can result in significant environmental damage, including spills of coal and other hazardous materials.
Ships
Shipping coal is a common method of transporting coal internationally, especially from countries with large coal reserves to countries with high demand for coal. Shipping can be an efficient way to transport large volumes of coal over long distances, and it can also be cost-effective. Ships can also be highly flexible, as they can access ports that may not be accessible to other types of transportation.
However, shipping coal can also result in water pollution and emissions of air pollutants. In addition, ships can be affected by weather conditions, piracy, and other logistical challenges.
Pipelines
Pipelines are another method of transporting coal, although this is less common than other methods. Pipelines can transport coal over long distances with minimal emissions, and they are not affected by traffic congestion or other logistical issues. In addition, pipelines can be highly reliable, as they are less prone to accidents and other disruptions than other types of transportation.
However, pipelines can be expensive to construct and maintain, and they can also be affected by leaks and other environmental issues.
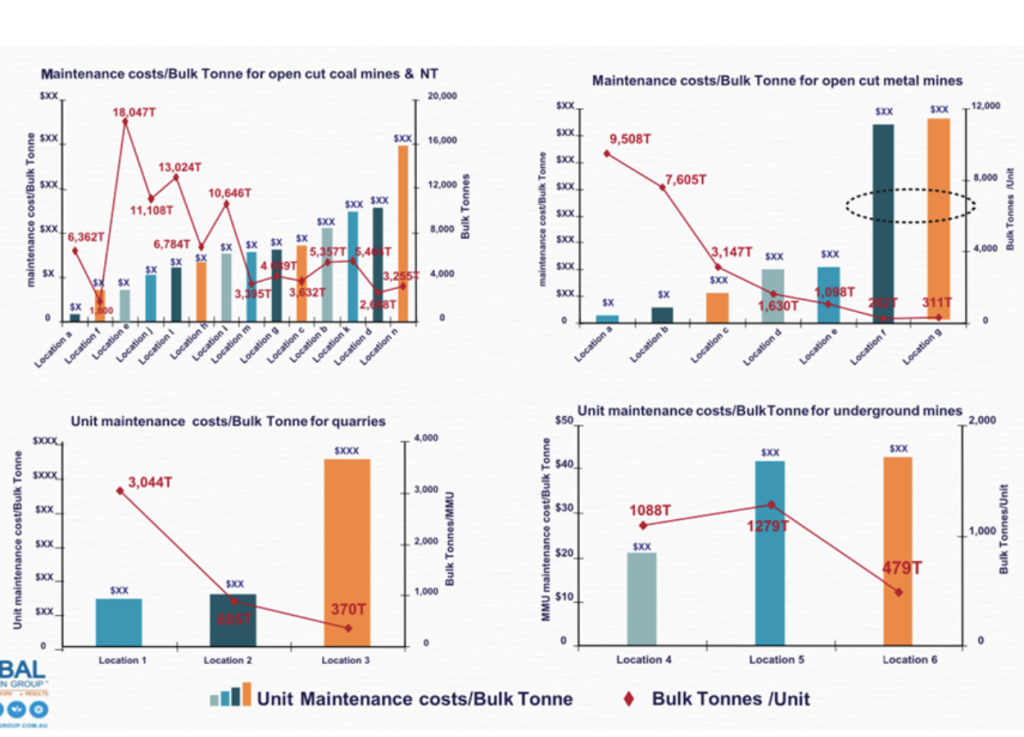
Unit Maintenance Cost
Unit maintenance costs in coal transport refer to the costs incurred in maintaining and repairing the equipment and infrastructure used to transport coal. This can include trucks, trains, ships, pipelines, and other types of transportation equipment, as well as the associated maintenance facilities and support services.Unit maintenance costs can be significant in coal transport, as the equipment and infrastructure used in this industry are often subject to harsh operating conditions and heavy wear and tear.
For example, trucks used to transport coal on unpaved roads may require frequent repairs and maintenance due to the harsh terrain and the weight of the coal.Similarly, trains and ships used to transport coal may require regular inspections and repairs to their engines, braking systems, and other components to ensure safe and efficient operation. Pipelines used to transport coal may require frequent inspections and repairs to prevent leaks or other failures.
The unit maintenance costs in coal transport can vary depending on a number of factors, including the type of equipment and infrastructure used, the operating conditions, and the frequency and intensity of use. Companies that operate in this industry must carefully manage their maintenance costs to ensure that their equipment and infrastructure are kept in good condition while minimizing the impact on their bottom line.
Overall, unit maintenance costs are an important consideration in coal transport, as they can significantly impact the efficiency and profitability of the industry. By carefully managing these costs and investing in high-quality equipment and infrastructure, companies can ensure the safe and reliable transportation of coal while minimizing the impact on their operating expenses.
Unit Maintenance cost for bulk quarries
Bulk quarries are typically located in remote areas and are subject to harsh operating conditions, which can result in increased wear and tear on the equipment and infrastructure used. The frequent transport of heavy loads and the exposure to extreme weather conditions can also result in additional maintenance and repair costs.
Effective maintenance and repair practices are essential for the safe and efficient operation of bulk quarries. Regular inspections and maintenance can help to prevent equipment failures and prolong the life of the machinery and infrastructure used. It is important to implement a comprehensive maintenance program that includes preventive maintenance, repair work, and replacement of worn or damaged parts.
The cost of maintenance and repair work for bulk quarries can vary depending on several factors, including the size and complexity of the operation, the type of machinery and equipment used, and the frequency and intensity of use. The cost of spare parts and replacement components can also impact maintenance costs.
Effective maintenance management is critical for bulk quarry operators to minimize their maintenance costs while ensuring the safe and efficient operation of their equipment and infrastructure. By implementing an effective maintenance program and investing in high-quality equipment and infrastructure, bulk quarry operators can improve their operational efficiency and reduce the impact of maintenance costs on their bottom line.
Unit Cost Maintenance cost for underground mines
Unit maintenance cost for underground mines refers to the cost incurred in maintaining and repairing the equipment and infrastructure used in underground mining operations. These costs include maintenance and repair expenses for drills, loaders, conveyor belts, ventilation systems, and other machinery and equipment used in the mining and transportation of materials.The frequent transport of heavy loads and the exposure to extreme conditions, such as heat, humidity, and dust, can also result in additional maintenance and repair costs.
Effective maintenance and repair practices are essential for the safe and efficient operation of underground mines. Regular inspections and maintenance can help to prevent equipment failures and prolong the life of the machinery and infrastructure used. It is important to implement a comprehensive maintenance program that includes preventive maintenance, repair work, and replacement of worn or damaged parts.
The cost of maintenance and repair work for underground mines can vary depending on several factors, including the size and complexity of the operation, the type of machinery and equipment used, and the frequency and intensity of use. The cost of spare parts and replacement components can also impact maintenance costs.
Effective maintenance management is critical for underground mine operators to minimize their maintenance costs while ensuring the safe and efficient operation of their equipment and infrastructure. By implementing an effective maintenance program and investing in high-quality equipment and infrastructure, underground mine operators can improve their operational efficiency and reduce the impact of maintenance costs on their bottom line.
Unit Cost Personnel
Personnel factors are an essential component of inland coal transportation and can significantly impact the efficiency and cost of operations. Some personnel factors that may affect inland coal transportation include:
- Experience and Training: Inland coal transportation companies need experienced and well-trained personnel to operate vehicles, load and unload coal, and maintain equipment. Personnel with inadequate training or experience may lead to increased incidents of accidents, errors, and downtime.
- Safety: Safety is a critical consideration in inland coal transportation, and personnel must adhere to established safety protocols and regulations to minimize the risk of accidents and injuries. Neglecting safety standards can result in higher insurance premiums, costly litigation, and damage to the reputation of the transportation company.
- Workforce Management: Effective management of the workforce is essential for ensuring that personnel are available, productive, and motivated. Personnel factors such as employee morale, job satisfaction, and turnover can impact transportation costs and efficiency.
- Compensation and Benefits: Personnel costs, including wages, benefits, and overtime pay, are a significant factor in the overall cost of inland coal transportation. To attract and retain qualified personnel, companies must offer competitive compensation and benefits packages.
- Unionization: Many transportation companies are unionized, and personnel factors such as collective bargaining, work stoppages, and strikes can significantly impact transportation costs and efficiency.
Factors affecting the cost of inland coal transportation
The cost of inland coal transportation is influenced by several factors, including:
- Distance: The distance between the mine and the final destination is a significant cost factor in inland coal transportation. Longer distances result in higher transportation costs due to increased fuel consumption, maintenance costs, and labor expenses.
- Mode of transportation: The mode of transportation used to move coal from the mine to the final destination also affects transportation costs. Rail and barge transportation are generally more cost-effective than truck transportation for longer distances.
- Infrastructure: The quality of infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and tunnels, can significantly impact transportation costs. Poor infrastructure can result in increased maintenance costs, slower transportation times, and higher fuel consumption.
- Fuel costs: The cost of fuel, such as diesel or gasoline, can significantly impact transportation costs. Fuel costs can vary depending on market conditions, and increases in fuel prices can result in higher transportation costs.
- Labor costs: Labor costs, including wages, benefits, and overtime pay, can be a significant cost factor in inland coal transportation. The number of personnel required to operate transportation vehicles, load and unload coal, and maintain equipment can impact overall transportation costs.
- Vehicle costs: The cost of purchasing, maintaining, and repairing transportation vehicles, such as trucks or railcars, can also impact transportation costs. Older or poorly maintained vehicles may require more frequent repairs and maintenance, which can result in higher costs.
- Regulatory compliance: Transportation companies must comply with various regulations related to safety, environmental protection, and transportation of hazardous materials. Compliance with these regulations can result in additional costs, such as training, equipment upgrades, and fees.
In This Project
The transport services for a coal and metal mine are provided by our client, who primarily operates in the Northern Territory and delivers to several locations. As the distance to these delivery sites increases, the cost of transportation also increases.
Our task was to enhance the supply chain efficiency and simplify the transportation of goods.
Our Recommendations
- Optimize routes and transportation modes: Analyze the transportation routes and modes used to move coal from the mine to the destination. Consider using more efficient modes of transportation, such as rail or barge, and optimize routes to reduce distance and travel time.
- Invest in technology: Implement modern technologies such as GPS tracking, telematics, and fleet management systems to track vehicle movements, monitor fuel consumption, and identify areas where cost savings can be made.
- Reduce fuel consumption: Take steps to reduce fuel consumption by optimizing vehicle maintenance, reducing idling time, and training drivers on fuel-efficient driving techniques.
- Improve load efficiency: Optimize the loading process to reduce the number of trips required to move the coal. Use larger vehicles or trailers to transport more coal in a single trip, and ensure that vehicles are fully loaded.
- Minimize downtime: Minimize downtime by ensuring that vehicles are well-maintained, and that repairs and maintenance are carried out on a regular basis. Reduce the time required to load and unload vehicles by implementing efficient loading and unloading processes.
- Negotiate transportation rates: Negotiate transportation rates with transport providers to ensure that costs are competitive and that rates are in line with market conditions.
- Use alternative fuels: Consider using alternative fuels, such as natural gas or electricity, to power transportation vehicles. While this may require an initial investment, it can result in significant cost savings over time.
Conclusions
Coal mining and transportation of coal are essential components of the global energy system, but they also have significant environmental and social impacts. It is important to understand these impacts and to work towards mitigating them through responsible mining practices and sustainable transportation methods. By doing so, we can ensure that we continue to have access to the energy we need while minimizing the negative impacts on the planet and its inhabitants.Open-cut metal mines are a type of mining operation used to extract metal ores from the earth. While they can be efficient and cost-effective, they also have significant environmental and social impacts, and it is important to manage these impacts through responsible mining practices and environmental management.
Transporting coal is an essential component of the global energy system, and a variety of methods are used to move coal from mines to power plants and other facilities. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it is important to weigh these factors carefully when choosing a transportation method. By doing so, we can ensure that we continue to have access to the energy we need while minimizing the negative impacts on the planet and its inhabitants. Additionally, it is important to work towards more sustainable and environmentally responsible methods of coal transportation, such as pipelines and cleaner fuels for trucks and trains.
bulk tonnes per unit refers to the amount of material that can be transported per unit of time using a particular type of transportation. This is an important measurement for transportation planning and logistics, and it helps ensure that the transportation system can meet the demand for the material being transported.
The key to successful cost savings in this industry is to maintain a focus on efficiency, safety, and reliability, while continually seeking opportunities to improve operations and reduce costs.
About the Author
 Vivek Sood: Sydney based managing director of Global Supply Chain Group, a strategy consultancy specializing in supply chains. More information on Vivek is available on www.linkedin.com/in/vivek and more information on Global Supply Chain Group is available www.globalscgroup.com
Vivek Sood: Sydney based managing director of Global Supply Chain Group, a strategy consultancy specializing in supply chains. More information on Vivek is available on www.linkedin.com/in/vivek and more information on Global Supply Chain Group is available www.globalscgroup.com
Vivek is the Managing Director of Global Supply Chain Group, a boutique strategy consulting firm specialising in Supply Chain Strategies, and headquartered in Sydney, Australia . He has over 24 years of experience in strategic transformations and operational excellence within global supply chains. Prior to co-founding Global Supply Chain Group in January 2000, Vivek was a management consultant with top-tier strategy consulting firm Booz Allen & Hamilton.
Vivek provides strategic operations and supply chain advice to boards and senior management of global corporations, private equity groups and other stakeholders in a range of industries including FMCG, food, shipping, logistics, manufacturing, chemicals, mining, agribusiness, construction materials, explosives, airlines and electricity utilities.
Vivek has served world-wide corporations in nearly 500 small and large projects on all continents with a variety of clients in many different industries. Most of projects have involved diagnostic, conceptualisation and transformation of supply chains – releasing significant amount of value for the business. His project work in supply chain management has added cumulative value in excess of $500M incorporating projects in major supply chain infrastructure investment decisions, profitable growth driven by global supply chain realignment, supply chain systems, negotiations and all other aspects of global supply chains.
Vivek has written a number of path breaking articles and commentaries that are published in several respected journals and magazines. Vivek has spoken at several supply chain conference, forums and workshops in various parts of the world. He has also conducted several strategic workshops on various aspects of supply chain management. He received his MBA with Distinction from the Australian Graduate School of Management in 1996 and prior to these studies spent 11 years in the Merchant Navy, rising from a Cadet to Master Mariner.
More information on Vivek is available on www.linkedin.com/in/vivek and more information on Global Supply Chain Group is available on www.globalscgroup.com
Related Posts
Click below to see related posts.

The Impact of Plummeting Shipping Container Prices Across Industries
Explore the far-reaching consequences of plummeting shipping container prices on diverse industries, revealing the intricate connections shaping global trade, supply chains, and economic landscapes.

Race Day Logistics: Intricacies of Pit Stop
Explore the race day’s heartbeat: the art of pit stops. Uncover the intricate logistics orchestrating split-second tire changes, refuels, and strategy adjustments that define Formula 1’s high-speed drama.

Mastering Travel Logistics in Formula 1 Racing
Discover the art of flawless travel logistics in the high-speed world of Formula 1. Uncover how precision planning and real-time coordination keep teams on track across the global circuit.
